Set up Kubernetes test environments for TestOps (Legacy)
This document covers TestOps Legacy version only.
This document demonstrates how to set up an AWS EKS Kubernetes test environment inside Katalon TestOps.
Kubernetes is an open-source platform that orchestrates container distribution for running test cases. It's like having an assistant to handle the containers for you.
See Kubernetes Overview to learn more about what Kubernetes is and what it can do.
Steps to set up a Kubernetes test environment
Note: The setup works best with Kubernetes version 1.25 or later.
To set up a Kubernetes test environment, follow these steps:
- Sign in to Katalon TestOps and go to TestOps Settings > Organization Setup.

This shows the Test Environments page. It also lists the agents you have.
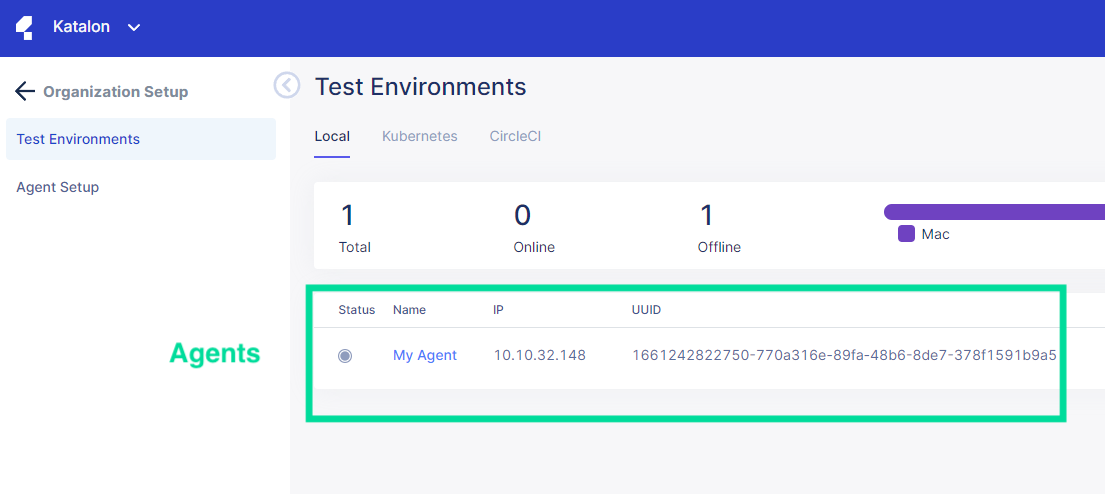
- Click Kubernetes to switch to the Kubernetes Test Environments page.
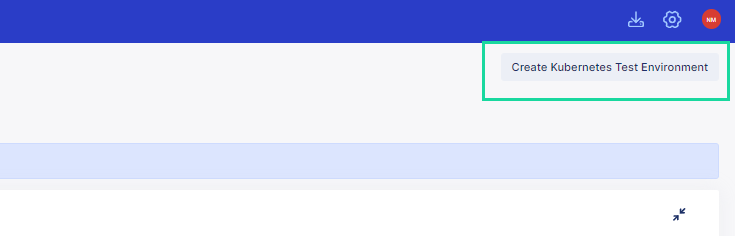
- Click the Create Kubernetes Test Environment button at the upper right corner.
- Fill in the information for your agent. The images below are taken from a AWS EKS dashboard:
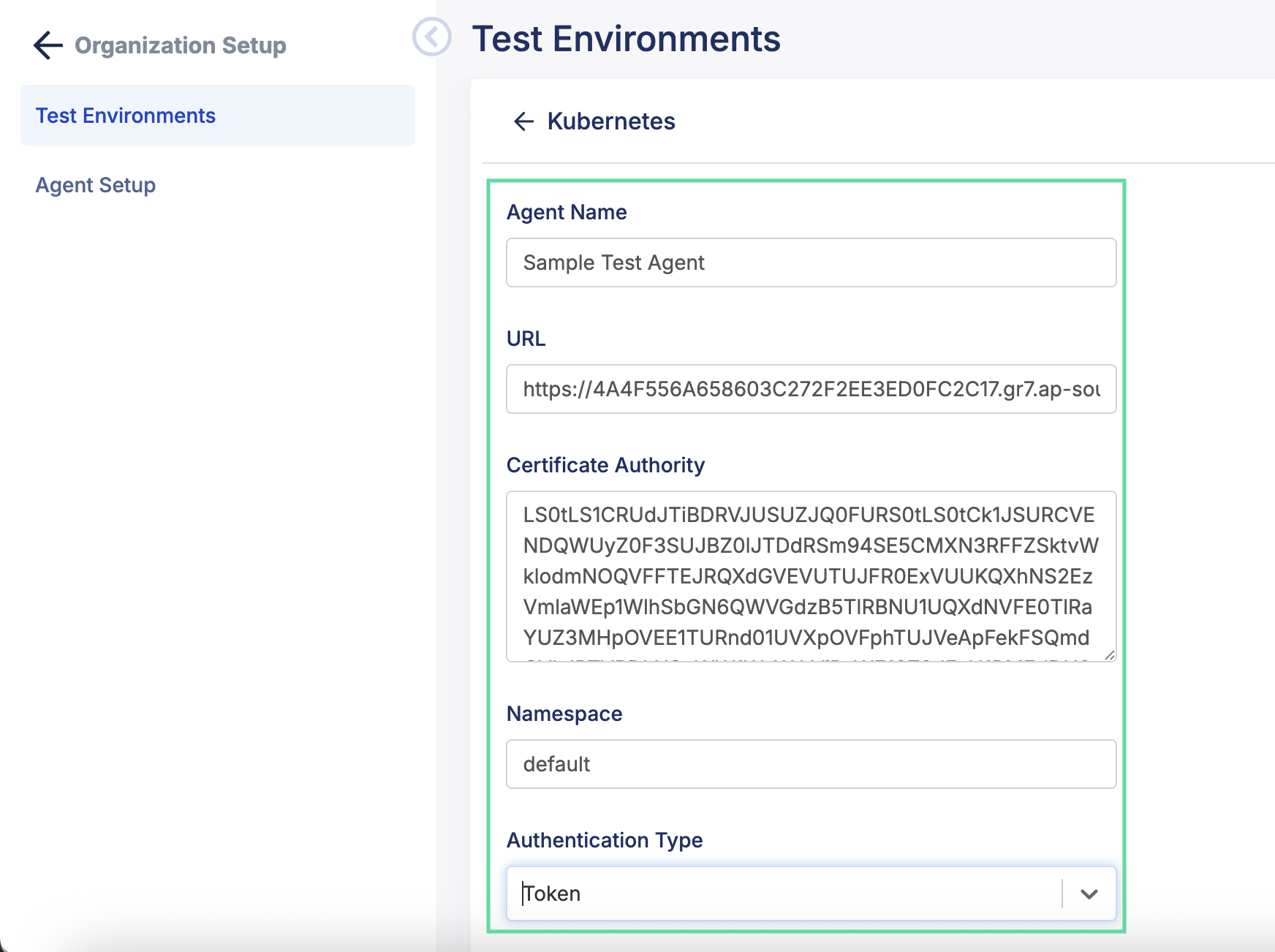
- Agent Name: The display name for your agent
- URL: The API server endpoint.
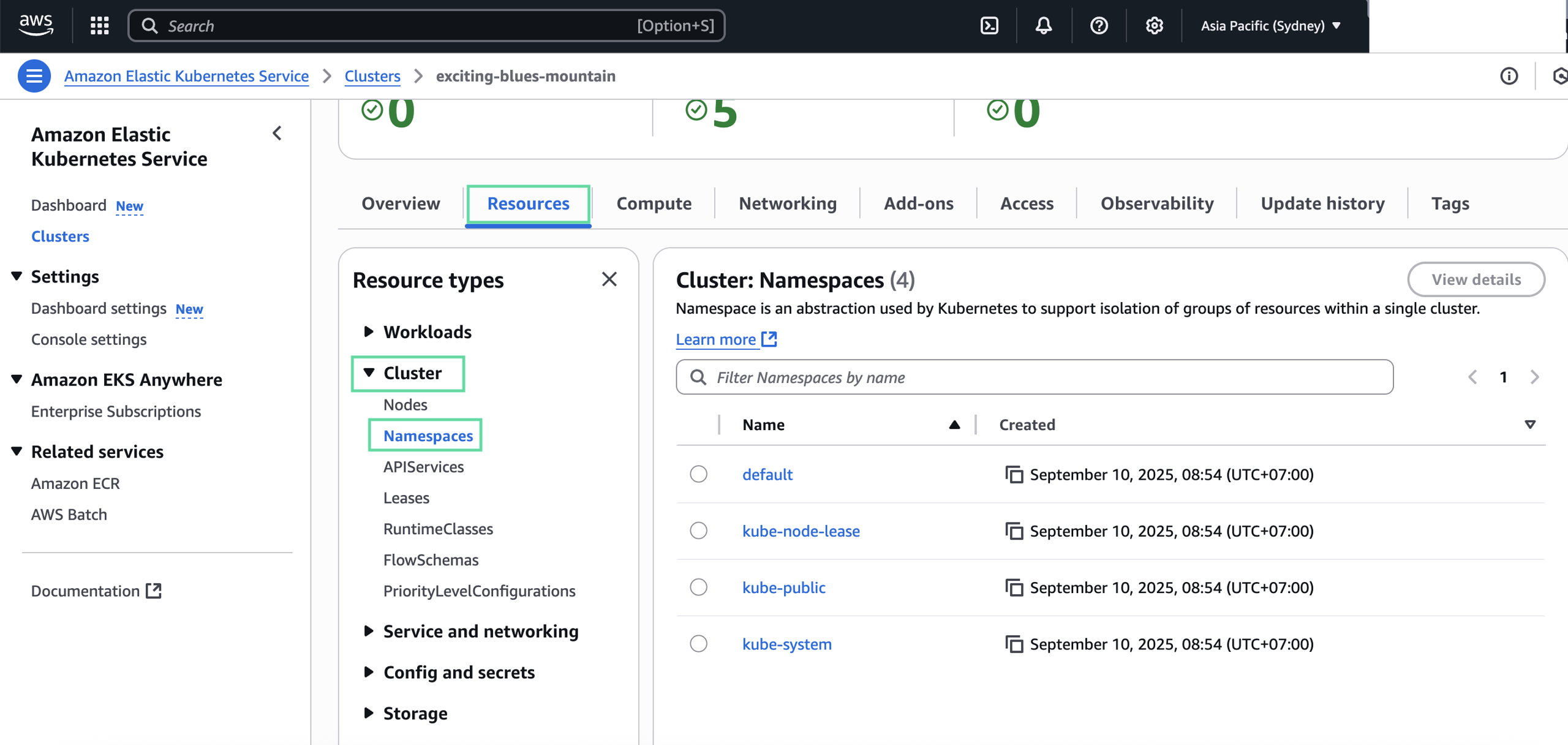
- Certificate Authority (CA): The content of your certificate authority. To get this information, go select your Kubernetes cluster in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service > Clusters, and it's listed in Overview > Details.
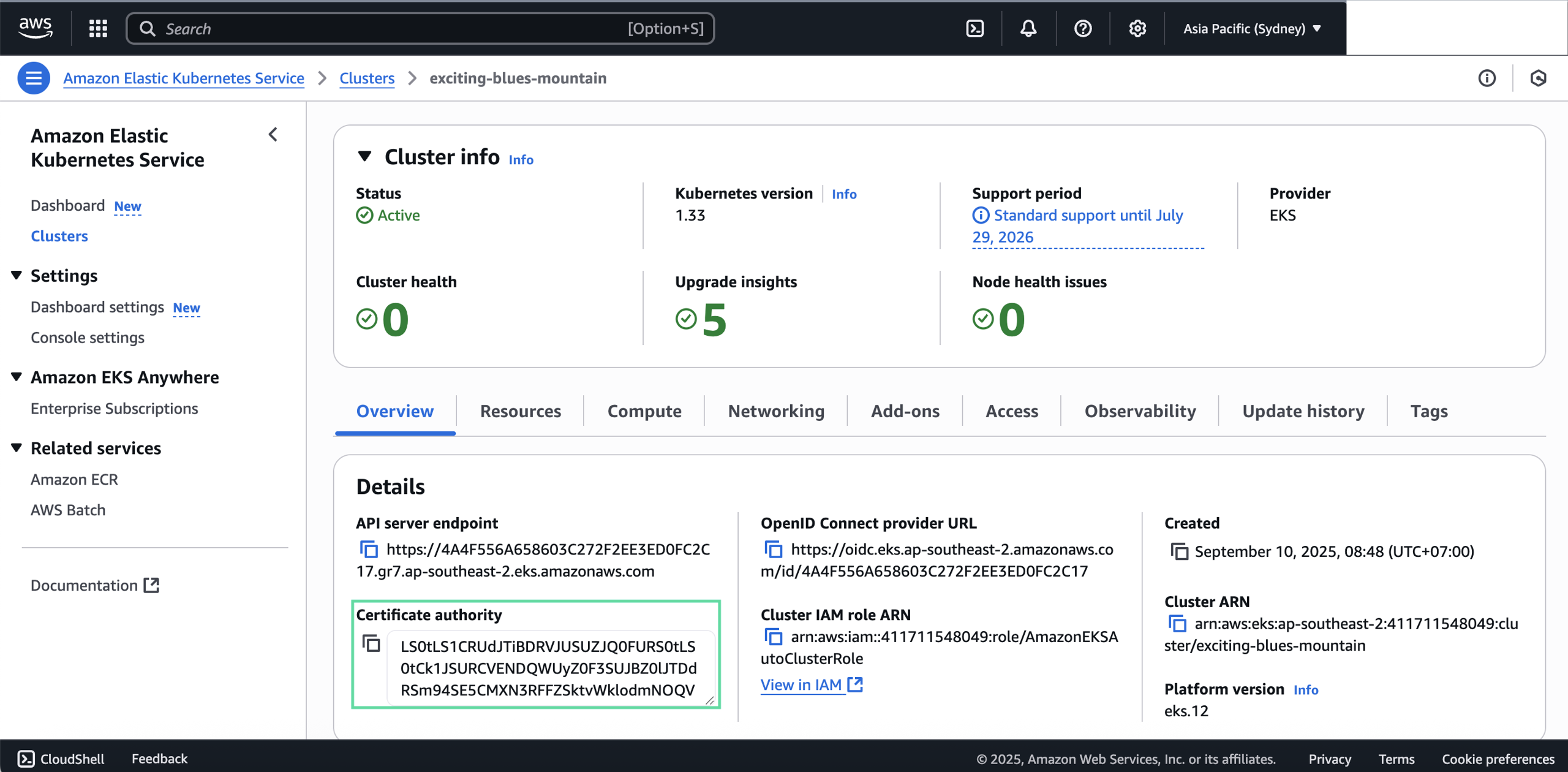
- Namespace: The namespace created for your Kubernetes cluster, can be viewed in Overview > Resource > Resource Types > Cluster > Namespaces
- Authentication Type: The authentication method to access Kubernetes environment (see more right below).
- Click Test Connection to ensure your information is correct.
- When the connection is correct, click Create.
Authentication Type
The Authentication Type section has a dropdown menu with 3 options: Username/Password, Token, or AWS EKS.
Username/Password
The username/password pair is a classic authentication method. If you've set up your Kubernetes cluster to have users, you can use this as the method of authentication.
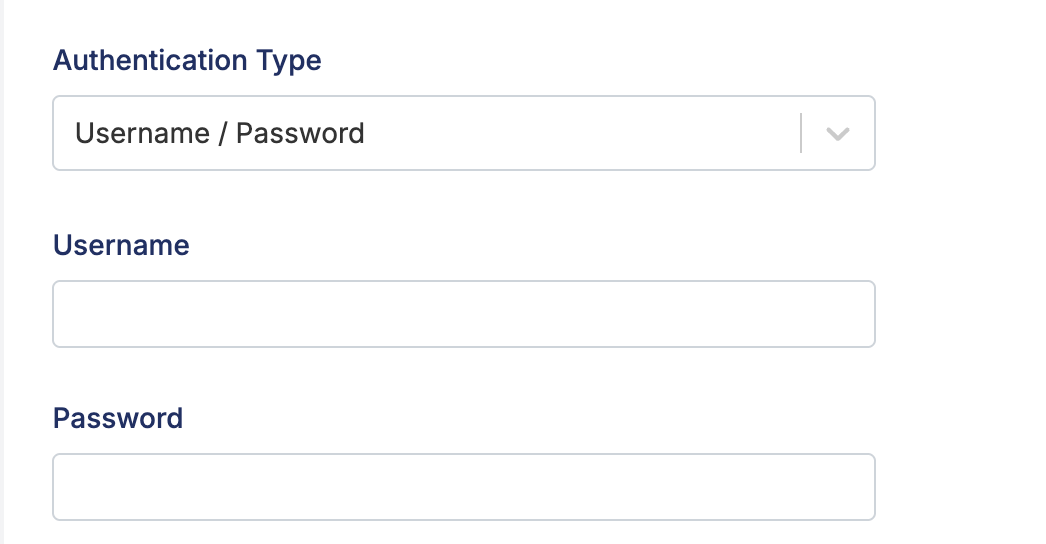
For example, in AWS EKS, they are the Identity and Access Management (IAM) user's username and password, often labeled as AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Access Key. See IAM users for more details.
As the root user creates an IAM user, they must first set a username. This is the string to fill in the Username field.
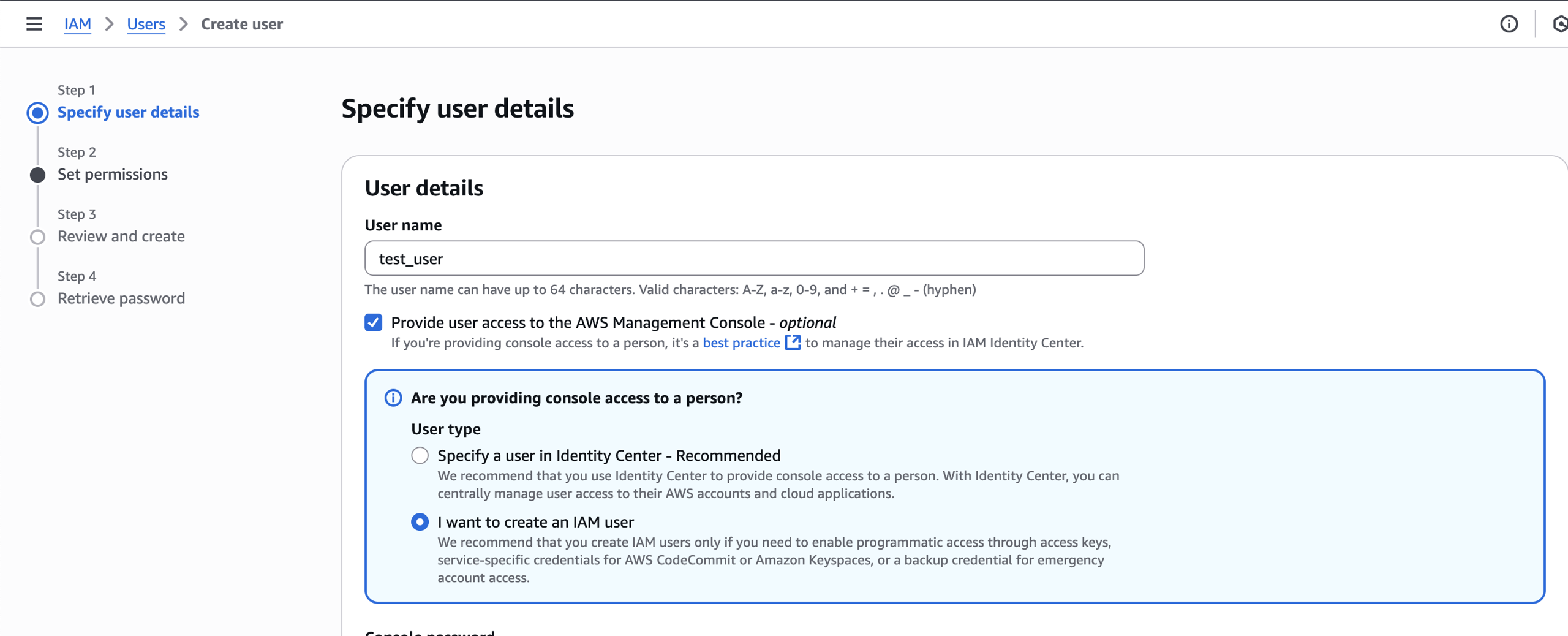
As for the Password field, there are two scenarios:
- The root user chooses to set a custom password: once the IAM user is created, use this password to fill in the “Password” field.
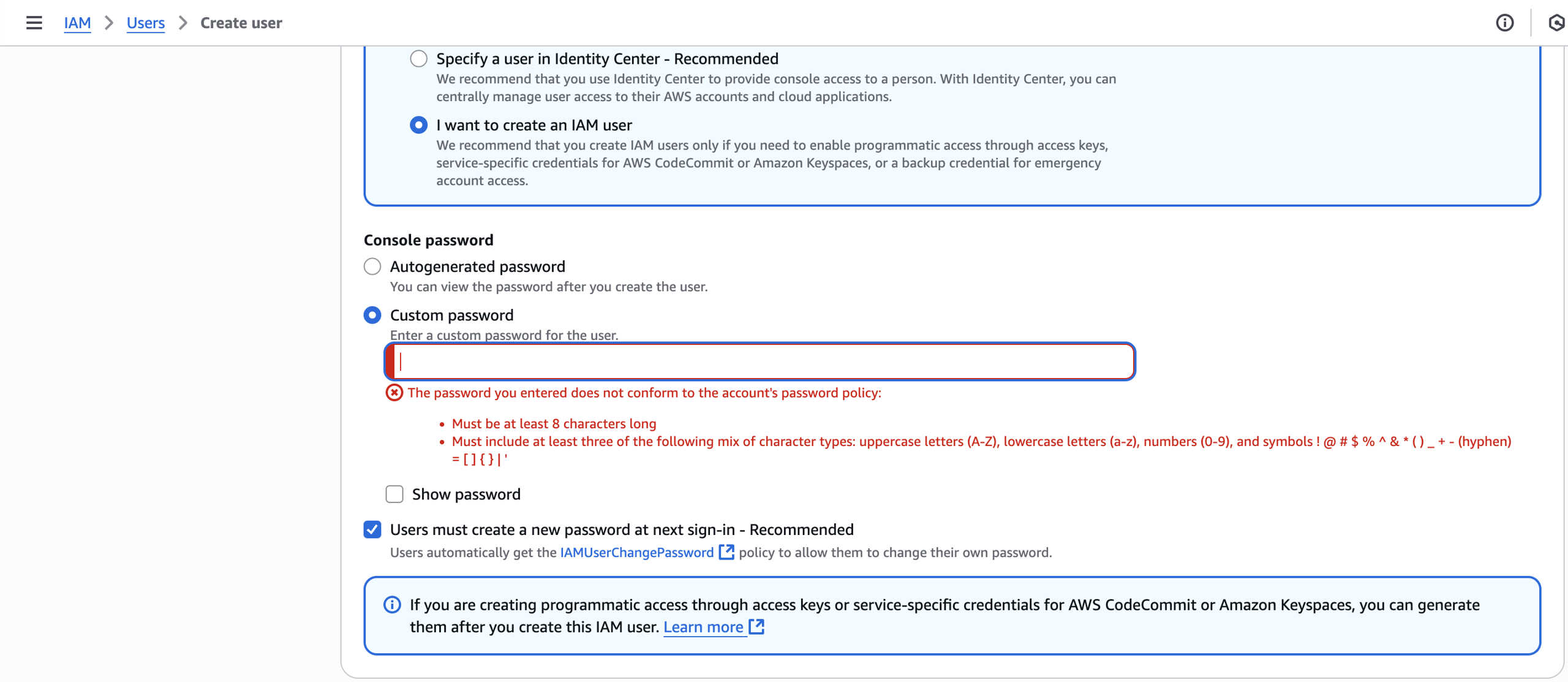
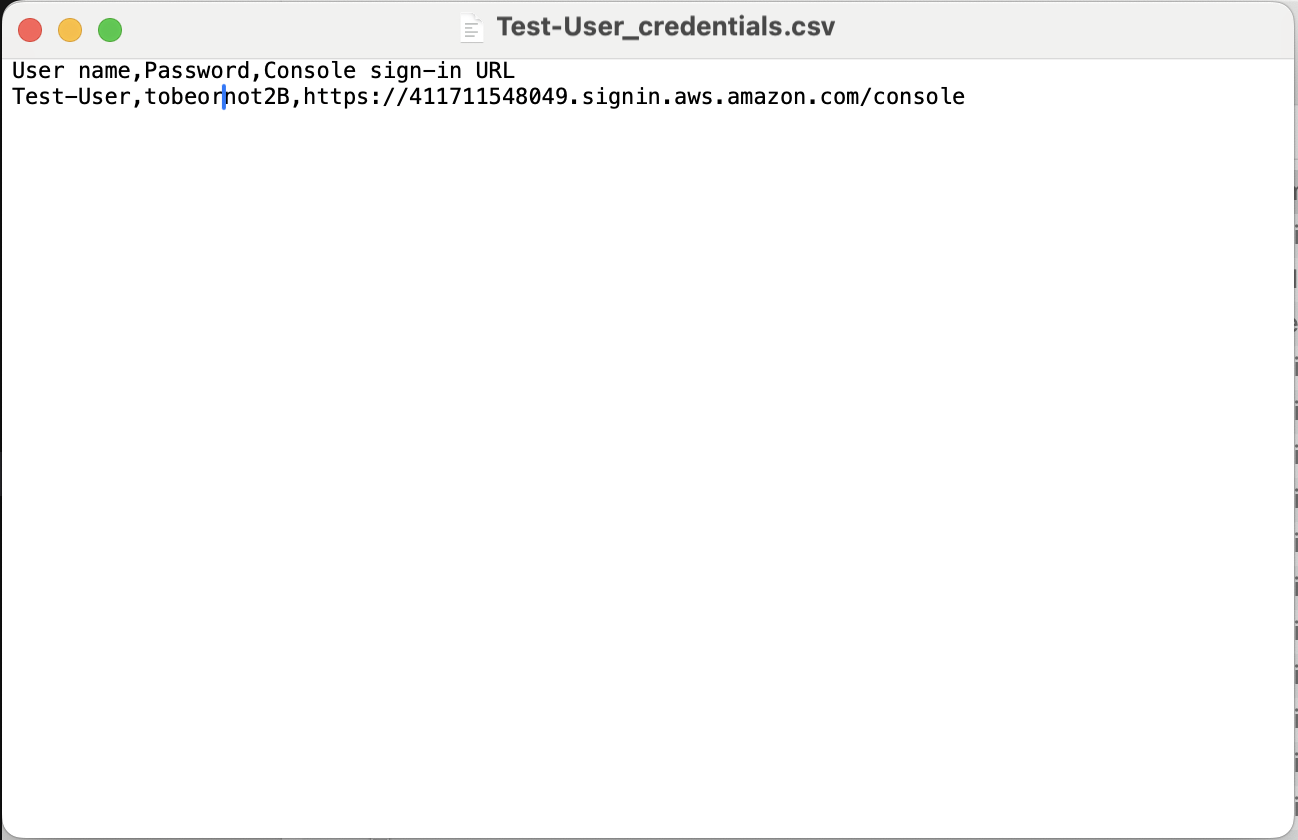
- The root user chooses to auto-generate a password: Once the IAM user is created, EKS asks the user to download credentials as a CSV file. Viewing the file shows both the Username and Password, like so:
Token
As an alternative to Username/Password, a token can be used as the authentication method.
For Kubernetes accounts created via kubectl: See kubectl Create Token to learn more about creating a token using kubectl.
For AWS EKS users: See Configure AWS CLI to configure a profile and see Get a token for authentication with an Amazon EKS cluster to see how to create an access token.
AWS EKS
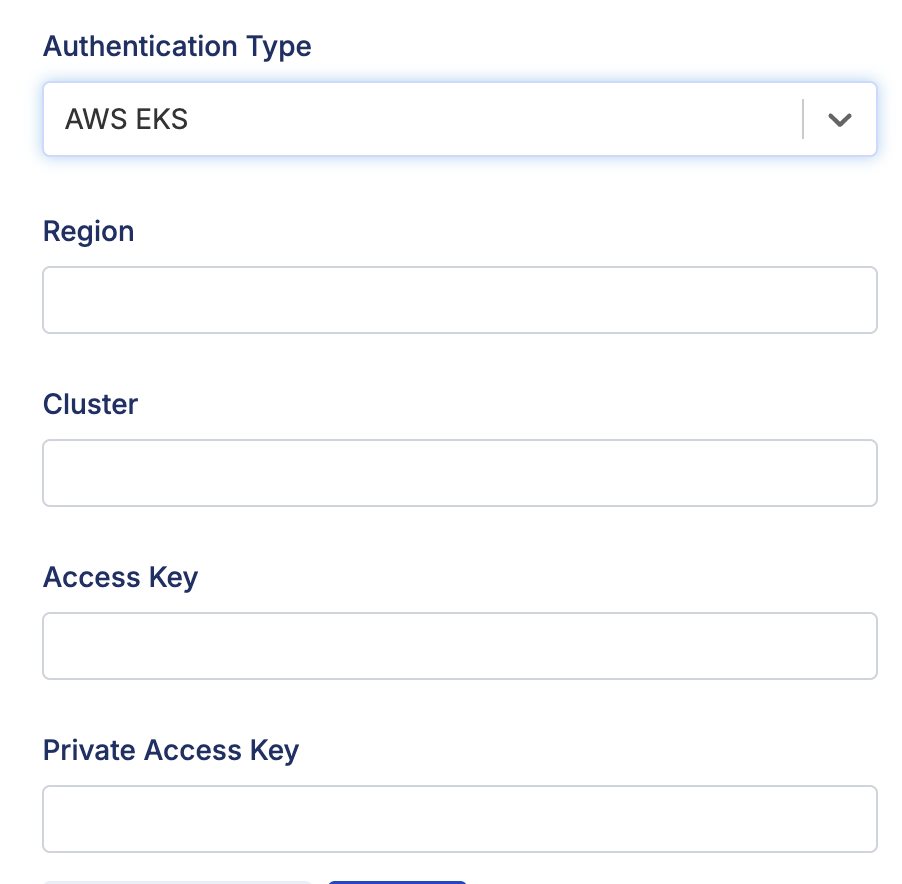
AWS EKS users can also choose this as the authentication method. The required fields are:
- Region: The region where your Kubernetes cluster was created.
- Cluster: The name of your cluster.
- Access Key: The IAM account's access key.
- Private Access Key: The IAM account's private access key.
Both the Access Key and Private Access Key can be found as you configure an AWS EKS profile. See Configure AWS CLI to configure a profile.